Step-by-step explanation:
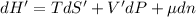
For ∝ phase system,
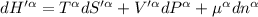
For β phase system,
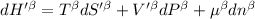
Now we know that the total enthalpy is the sum of the enthalpy in the alpha and beta phases.
∴
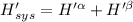
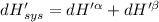
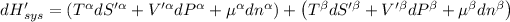
Now P, S an n are constants.
Then for isolated system, we get,
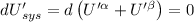
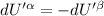
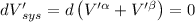
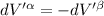
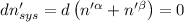
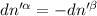
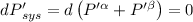
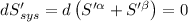
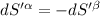
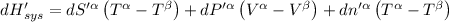
For equilibrium,
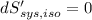
Then
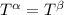 ----- for thermal equilibrium
----- for thermal equilibrium
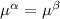 ----- for chemical equilibrium
----- for chemical equilibrium
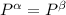 ----- for mechanical equilibrium
----- for mechanical equilibrium
The above conditions are valid for one component two phase system.