To develop this problem it is necessary to apply the optical concepts related to the phase difference between two or more materials.
By definition we know that the phase between two light waves that are traveling on different materials (in this case also two) is given by the equation
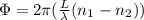
Where
L = Thickness
n = Index of refraction of each material
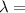 Wavelength
Wavelength
Our values are given as
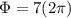
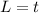
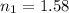
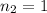
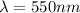
Replacing our values at the previous equation we have
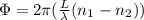
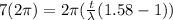
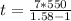
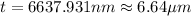
Therefore the thickness of the mica is 6.64μm