Answer:
99203s⁻¹
Step-by-step explanation:
Turnover number is defined as the maximum number of chemical conversions of substrate molecules per second that a single catalytic site will execute for a given enzyme concentration.
It is possible to calculate this number using the maximum reaction rate (Vmax) and catalyst site concentration, thus:
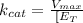
As umol are 1x10⁻⁶ moles and nmol are 1x10⁻⁹ moles:
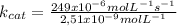
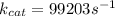
I hope it helps!