Answer:
The coefficient of static friction is 1.13x10⁻⁵.
Step-by-step explanation:
We can find the coefficient of static friction as follows:
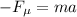
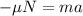
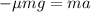
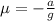 (1)
(1)
Where:
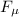 : is the friction force
: is the friction force
m: is the mass of the box
a: is the acceleration
g: is the gravity = 9.81 m/s²
First, we need to calculate the acceleration:
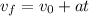 (2)
(2)
Where:
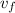 is the final speed of the box = 0
is the final speed of the box = 0
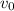 is the initial speed of the box
is the initial speed of the box
t is the time = 600 s
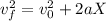 (3)
(3)
Where:
X: is the distance traveled by the box = 20 m
By solving equation (2) for
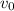 and by entering into equation (3) we have:
and by entering into equation (3) we have:
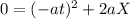

Now, we can calculate the coefficient of static friction by entering the above value into equation (1) :
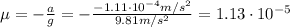
Therefore, the coefficient of static friction is 1.13x10⁻⁵.
I hope it helps you!