Answer: The partial pressure of nitrogen gas is 405.76 mmHg and that of hydrogen gas is 257.24 mmHg
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
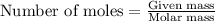
Given mass of nitrogen gas = 3.46 g
Molar mass of nitrogen gas = 28 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
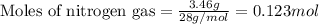
Given mass of hydrogen gas = 0.156 g
Molar mass of hydrogen gas = 2 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
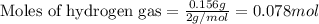
Mole fraction of a gas is calculated by using the formula:
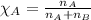 ......(1)
......(1)
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
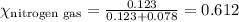
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
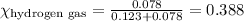
The partial pressure of a gas is given by Raoult's law, which is:
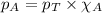 ......(2)
......(2)
where,
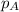 = partial pressure of substance A
= partial pressure of substance A
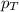 = total pressure = 663 mmHg
= total pressure = 663 mmHg
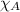 = mole fraction of substance A
= mole fraction of substance A

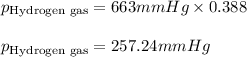
Hence, the partial pressure of nitrogen gas is 405.76 mmHg and that of hydrogen gas is 257.24 mmHg