Answer:
V= 0.147 L
Step-by-step explanation:
This is simply the application of combined gas law twice, to find the unknowns.
Combined gas law states that:
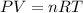
P= pressure of air
V= volume of air
n= moles of air
R= Universal gas constant ( 0.08205 L atm mol⁻¹ K⁻¹)
T= Absolute temperature in kelvin.
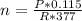
Now, applying the same gas law at 483K and substituting for n
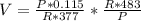
V=
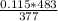
V= 0.147 L