Answer : The value of
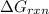 is, -27.0kJ/mole
is, -27.0kJ/mole
Explanation :
The formula used for
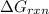 is:
is:
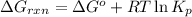 ............(1)
............(1)
where,
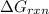 = Gibbs free energy for the reaction
= Gibbs free energy for the reaction
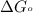 = standard Gibbs free energy = -32.8 kJ
= standard Gibbs free energy = -32.8 kJ
/mol
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mole.K
T = temperature = 298 K
 = equilibrium constant
= equilibrium constant
First we have to calculate the value of
 .
.
The given balanced chemical reaction is,
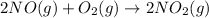
The expression for equilibrium constant will be :
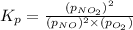
In this expression, only gaseous or aqueous states are includes and pure liquid or solid states are omitted.
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get
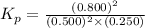
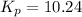
Now we have to calculate the value of
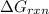 by using relation (1).
by using relation (1).
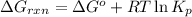
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get:
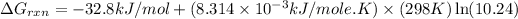
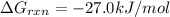
Therefore, the value of
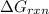 is, -27.0kJ/mole
is, -27.0kJ/mole