To solve this problem it is necessary to apply the concepts of thermal expansion. Thermal expansion can be expressed in longitudinal terms such as
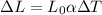
Where,
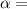 Thermal Expanssion Coefficient
Thermal Expanssion Coefficient
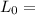 Initial Length
Initial Length
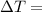 Change in Temperature
Change in Temperature
Our values are given as
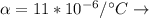 from Steel
from Steel
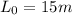
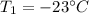
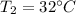
Replacing we have that,
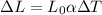
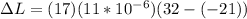
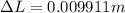
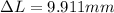
Therefore the difference in length of the beam between these two temperature extremes is 9.911mm