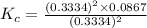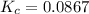Answer:
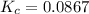
Step-by-step explanation:
Moles of SO₃ = 0.760 mol
Volume = 1.50 L
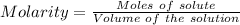
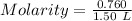
[SO₃] = 0.5067 M
Considering the ICE table for the equilibrium as:
![\begin{matrix} & 2SO_3_((g)) & \rightleftharpoons & 2SO_2_((g)) & + & O_2_((g))\\At\ time, t = 0 & 0.5067 &&0&&0 \\ At\ time, t=t_(eq) & -2x &&2x&&x \\----------------&-----&-&-----&-&-----\\Concentration\ at\ equilibrium:- &0.5067-2x&&2x&&x\end{matrix}]()
Given:
Equilibrium concentration of O₂ = 0.130 mol
Volume = 1.50 L
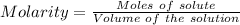
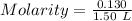
[O₂] = x = 0.0867 M
[SO₂] = 2x = 0.1733 M
[SO₃] = 0.5067-2x = 0.3334 M
The expression for the equilibrium constant is:
![K_c=\frac {[SO_2]^2[O_2]}{[SO_3]^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/d3uk4u1stuvyg6uiv6dwu05eurnb5gzt2u.png)