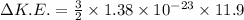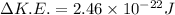Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
no of moles
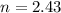
Temperature raised
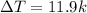
Work done by gas
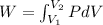
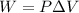
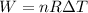
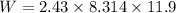
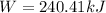
(b)Energy Transferred as heat
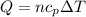
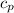 =specific heat at constant Pressure
=specific heat at constant Pressure
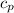 for ideal Mono atomic gas is
for ideal Mono atomic gas is
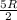
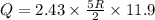
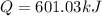
(c)Change in Internal Energy
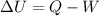
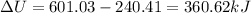
(d)Change in average kinetic Energy
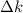
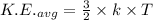
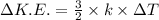 ,where k=boltzmann constant
,where k=boltzmann constant