Answer: The pressure of NO and
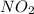 in the mixture is 0.58 atm and 0.024 atm respectively.
in the mixture is 0.58 atm and 0.024 atm respectively.
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Equilibrium partial pressure of
 = 0.29 atm
= 0.29 atm
For the given chemical equation:
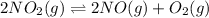
Initial: a
At eqllm: a-2x 2x x
Calculating for the value of 'x'
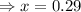
Equilibrium partial pressure of NO = 2x = 2(0.29) = 0.58 atm
Equilibrium partial pressure of
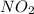 = a - 2x = a - 2(0.29) = a - 0.58
= a - 2x = a - 2(0.29) = a - 0.58
The expression of
 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
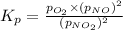
We are given:
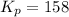
Putting values in above expression, we get:
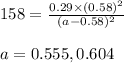
Neglecting the value of a = 0.555 because it cannot be less than the equilibrium concentration.
So,
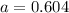
Equilibrium partial pressure of
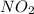 = (a - 0.58) = (0.604 - 0.58) = 0.024 atm
= (a - 0.58) = (0.604 - 0.58) = 0.024 atm
Hence, the pressure of NO and
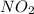 in the mixture is 0.58 atm and 0.024 atm respectively.
in the mixture is 0.58 atm and 0.024 atm respectively.