Answer:
The correct answer is A) 1.6 x 10-6
Step-by-step explanation:
A weak monoprotic acid has the following dissociation equilibrium. At the beggining (t=0), the concentration of the monoprotic acid (HA) is equal to 0.10 M and the concentration of the ions H⁺ and A⁻ is zero (no dissociation). At a time t, dissociation occur and there is x concentration of H⁺ and A⁻ which is given by the dissociation constant Ka.
HA(aq) ⇄ H⁺(aq) + A⁻(aq)
t=0 0.10 M 0 0
t -x +x +x
eq 0.10 M-x x x
Ka=
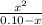
As the pH is 3.40, we can calculate the concentration of both H⁺ and A⁻, as follows:
pH= - log (conc H⁺)= -log x
⇒ x =
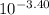 = 3.98 x 10⁻⁴
= 3.98 x 10⁻⁴
Now we introduce x in the previous equation to calculate Ka:
Ka=
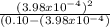
Ka= 1.59 x 10⁻⁶ ≅ 1.60 x 10⁻⁶