Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
a.) To find Secrional liftSectional lift Coefficient
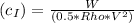
where Rho = 1.225Kg/m³ (density of air at sea level)
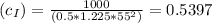
b.) To obtain the sectional induced coefficient:
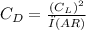
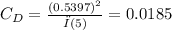
C.) For the effective angle of attack ∝0
∝0 =
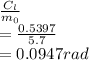
For induced angle of attack ∝i:
∝i=
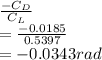
For absolute angle of attack ∝a:
∝a = ∝0 - ∝i = 0.0947 - (-0.0343) = 0.1290 rad
For geometric angle of attack ∝g:
∝g = ∝a + ∝L given ∝L = -2°≅-0.0349 rad
= 0.1290-0.0349 = 0.0941rad