Answer:
The current lags the potential difference by π/2 in an inductor
Step-by-step explanation:
The potential difference leads to the current by
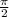 . Alternate signals such as current and voltage -in this case- are periodic, this means that this signals are repeated at fixed spaces of time. Thus, In an inductor the current lags the potential difference by
. Alternate signals such as current and voltage -in this case- are periodic, this means that this signals are repeated at fixed spaces of time. Thus, In an inductor the current lags the potential difference by
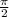 .
.