Answer: The concentration of
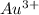 is
is

Step-by-step explanation:
The given chemical cell follows:
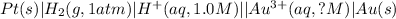
Oxidation half reaction:
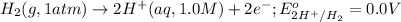 ( × 3)
( × 3)
Reduction half reaction:
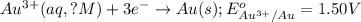 ( × 2)
( × 2)
Net cell reaction:
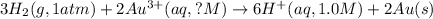
Oxidation reaction occurs at anode and reduction reaction occurs at cathode.
To calculate the
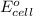 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
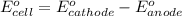
Putting values in above equation, we get:
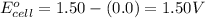
To calculate the EMF of the cell, we use the Nernst equation, which is:
![E_(cell)=E^o_(cell)-(0.059)/(n)\log ([H^(+)]^6)/([Au^(3+)]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/adv53sl8ysfeltus2ja8av8r68d24hn0aa.png)
where,
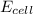 = electrode potential of the cell = 1.23 V
= electrode potential of the cell = 1.23 V
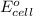 = standard electrode potential of the cell = +1.50 V
= standard electrode potential of the cell = +1.50 V
n = number of electrons exchanged = 6
![[H^(+)]=1.0M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/58e1m3vhdu02fgnksg1dzzwqcokti13bjy.png)
![[Au^(3+)]=?M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/z21daw2s36sqlwigpedob70yre6kg1cble.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![1.23=1.50-(0.059)/(6)* \log(((1.0)^6)/([Au^(3+)]^2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/f87l57s0cebhoq59s9zpdv9kl79zhwr1n6.png)
![[Au^(3+)]=-1.0906* 10^(-6),1.096* 10^(-6)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/pbw37wz6kuo6xfat554jjawwxlbavjihnf.png)
Neglecting the negative value because concentration cannot be negative.
Hence, the concentration of
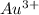 is
is
