Answer:
3.2 C
Step-by-step explanation:
e = Charge of electron =
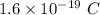
Number of synapses =
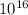
Signals transferred by each synapse 1000 calcium ions
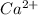
Each calcium ion carries 2 charges
Number of charges would be
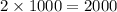
Total charges would be
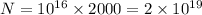
Charge is given by
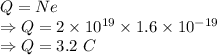
The total electric charge transfer in coulombs during that short time interval is 3.2 C