Answer:
the point-slope form of the equation: y + 3 = -³/₂(x - 2)
the slope-intercept form of the equation: y = -³/₂x
standard form of the equation: 3x + 2y = 0
Explanation:
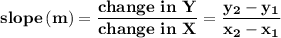
(-2, 3) ⇒ x₁ = -2, y₁ = 3
(2, -3) ⇒ x₂ = 2, y₂ = -3
So the slope:
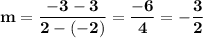
The point-slope form of equation is : y - y₀ = m(x - x₀), where (x₀, y₀) is any point the line passes through.
(2, -3) ⇒ x₀ = 2, y₀ = -3
Therefore:
y + 3 = -³/₂(x - 2) ← the point-slope form of the equation
y + 3 = -³/₂x + 3
y = -³/₂x ← the slope-intercept form of the equation (b=0)
y + ³/₂x = 0
3x + 2y = 0 ← standard form of the equation