To solve this problem it is necessary to apply the continuity equations for which it is defined that the proportion of Area in the initial section is equal to the final section. In other words,
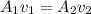
Where,
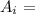 Cross sectional area at each section
Cross sectional area at each section
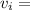 Velocities of fluid at each section
Velocities of fluid at each section
The total area of the branch is eighteen times of area of smaller artery. The average cross-sectional area of each artery is
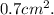
Therefore the Cross-sectional area at the end is
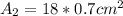
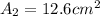
Applying the previous equation we have then
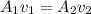
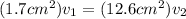
The ratio of the velocities then is
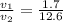
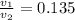
Therefore the factor by which the velocity of blood will reduce when it enters the smaller arteries is 0.1349