Answer:
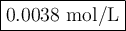
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Calculate the initial moles of acid and base
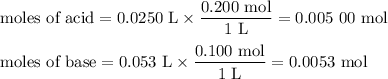
2. Calculate the moles remaining after the reaction
OH⁻ + H₃O⁺ ⟶ 2H₂O
I/mol: 0.0053 0.005 00
C/mol: -0.00500 -0.005 00
E/mol: 0.0003 0
We have an excess of 0.0003 mol of base.
3. Calculate the concentration of OH⁻
Total volume = 53 mL + 25.0 mL = 78 mL = 0.078 L
![\text{[OH}^(-)] = \frac{\text{0.0003 mol}}{\text{0.078 L}} = \textbf{0.0038 mol/L}\\\\\text{The final concentration of OH$^(-)$ is $\large \boxed{\textbf{0.0038 mol/L}}$}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/bwvsyj63tdu0islntkgxjua130p4cdea3m.png)