Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The expression relating length and time period
T = 2π
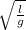
3.2 =
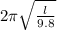
l = 2.54 m
On Mars g = 3.7
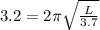
L = .96 m
b )
Expression for elastic constant and time period is as follows
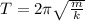
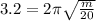
m = 5.19 N/s
Time period of oscillation due to spring is not dependent on g , so same time period will be found on Mars as that on the earth.