Answer:
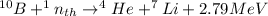
Step-by-step explanation:
BNCT therapy consists in the irradiation of the atoms of ¹⁰B that are contained in the tissue that has the tumor cells, with thermal neutrons to produce alpha particles and ⁷Li nucleus, according to the following nuclear reaction:
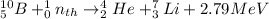
Since the tissues also contain H and N atoms, the neutron irradiation produces secondary reactions in which proton particles and gamma radiation are produced:
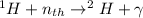
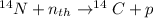
I hope it helps you!