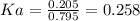Answer:
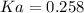
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the dissosiation factor of the HIn first we need to determine the concentration of ions in the solution. To do that we use the Lambert-Beer's law:
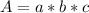
Where:
A is the absorbance
a is the absorptivity
b is the length of the cuvette
c is the concentration
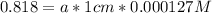
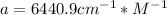
With this absorptivity we can calculate the concentration of HIn and In:
![x_{HIn]+x_(In)=1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/973wxcd9nx91ztz73rjvaw9dfpmrb93r5k.png)
![x_{HIn]=1-x_(In)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8hn5ah5nzalqaokradxj104j46nytgg68j.png)
![a=x_(In)*20060cm^(-1)*M^(-1)+ x_{HIn]*2929cm^(-1)*M^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ohly47yuw2o8rxjiwnac044v6fbv8f3gzv.png)
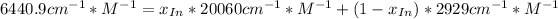
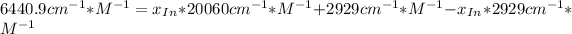
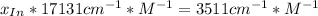
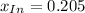
![x_{HIn]=1-0.205=0.795](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/sov2pyrhpikwqx9yr5x5ur7ezzna2kqwc8.png)
For the Ka:
![Ka=([In])/([HIn])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/a2i04spyc28n1vanmhog8hp4joox6efbk7.png)