Answer:
19,26 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The work done when a gas expand with a constant atmospheric pressure is:
W = PΔV
Where P is pressure and ΔV is the change in volume of gas.
Assuming the initial volume is 0, the reaction of 500g of Zn with H⁺ (Zn(s) + 2H⁺(aq) → Zn²⁺(aq) + H₂(g)) produce:
500,0g Zn(s)×
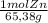 ×
×
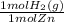 = 7,648 moles of H₂
= 7,648 moles of H₂
At 1,00atm and 303,15K (30°C), the volume of these moles of gas is:
V = nRT/P
V = 7,648mol×0,082atmL/molK×303,15K / 1,00atm
V = 190,1L
That means that ΔV is:
190,1L - 0L = 190,1L
And the work done is:
W = 1atm×190,1L = 190,1atmL.
In joules:
190,1 atmL×
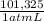 = 19,26 kJ
= 19,26 kJ
I hope it helps!