Answer:
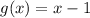
Explanation:
Any problem of this kind should first be approached by solving the initial function.
This question is based on curve translation on x-axis. But, there can be questions asked on translation in both axes, rotation of curve about origin, or both combined.
Initial function f(x) is a straight line from picture.
Common equation of straight line is
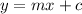
m= slope of the line
c= y-intercept
Slope of the line:
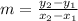
Let those points on graph be A(3,0) and B(0,-6)
Therefore, slope of line AB, using formula is:
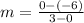
m=2
And c=(-6)
And equation of line AB is:
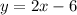
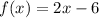
Now this line is translated backwards by 2 units, (x) becomes (x+2)
Let us consider a X, such that,
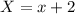
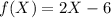
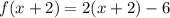
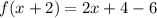
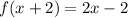
Now, there is another function such that,
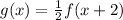
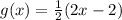
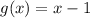 ; according to your question.
; according to your question.
In the picture, they are asking for a function,
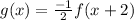
Then,
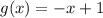 ; according to the picture.
; according to the picture.
Here, I have attached a file showing all the graphs for clear understanding.