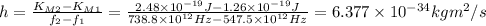Answer:
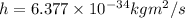
Step-by-step explanation:
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is given by the formula
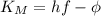 .
.
We have two situations where for
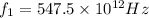 we get
we get
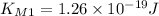 and for
and for
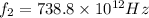 we get
we get
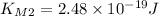 , so we have:
, so we have:
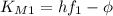
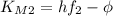
We can eliminate
 by substracting the first equation to the second:
by substracting the first equation to the second:
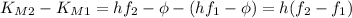
Which means: