Answer:
5.4 rad/s
48.6 m/s
5.4 m/s²
262.44 m/s²
Step-by-step explanation:
r = Radius of centrifuge = 9 m
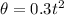
Differentiating with respect to time
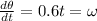
At t = 9 s
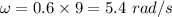
Angular velocity is 5.4 rad/s
Linear speed
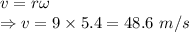
The linear speed of the astronaut is 48.6 m/s
Differentiating
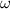 with respect to time
with respect to time
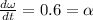
Tangential acceleration is given by
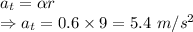
Tangential acceleration of the astronaut is 5.4 m/s²
Radial acceleration is given by
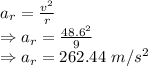
The radial acceleration of the astronaut is 262.44 m/s²