To develop the problem it is necessary to apply the concepts related to Magnetic Field.
The magnetic field is defined as
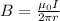
Where,
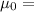 Permeability constant in free space
Permeability constant in free space
r = Radius
I = Current
Our values are given as,
B = 0.1T
d = 4.5mm
r = 2.25mm
If the maximum current that the wire can carry is I, then
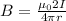
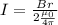
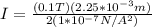
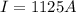
Therefore the maximum current is 1125A