Answer:
Null Hypothesis:
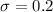
Alternative hypothesis:
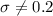 (Changes on the deviation)
(Changes on the deviation)
Explanation:
s represent the sample standard deviation
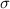 represent the population standard deviation (variable of interest)
represent the population standard deviation (variable of interest)
 represent the value that we want to test
represent the value that we want to test
n represent the sample size
A hypothesis is defined as "a speculation or theory based on insufficient evidence that lends itself to further testing and experimentation. With further testing, a hypothesis can usually be proven true or false".
The null hypothesis is defined as "a hypothesis that says there is no statistical significance between the two variables in the hypothesis. It is the hypothesis that the researcher is trying to disprove".
The alternative hypothesis is "just the inverse, or opposite, of the null hypothesis. It is the hypothesis that researcher is trying to prove".
Based on this the system of hypothesis should be:
Null Hypothesis:
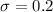
Alternative hypothesis:
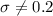 (Changes on the deviation)
(Changes on the deviation)
In order to test these system of hypothesis we need to select a significance level
 , then we need to calculate an statistic given by this formula.
, then we need to calculate an statistic given by this formula.
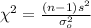
Then we need to calculate the degrees of freedom for the statistic on this case
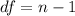
And after this we need to calculate the pvalue based on the significance, the alternative hypothesis and the statistic calculated.
If the
 we reject the null hypothesis
we reject the null hypothesis
If the
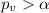 we FAIL reject the null hypothesis
we FAIL reject the null hypothesis