Answer:
Only the daughters will be carriers and the probability is 1 or 100%
Step-by-step explanation:
Homozygous dominant female =
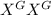
Affected male =
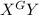
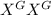 x
x
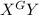
Offspring =
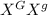 (female),
(female),
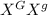 (females),
(females),
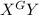 (male),
(male),
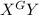 (male)
(male)
For X-linked traits, male gender can either be affected or not affected, they cannot be carriers because the Y chromosome is hypothesized to not carry any gene. Since the two X chromosomes in female carry genes, they can be carriers for X-linked traits.
Considering the female children only, the probability is 1 or 100%.