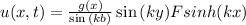Answer:
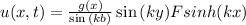
Explanation:
The Laplace's equation in rectangular coordinates is:
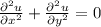
For the solution, we assume that u can be write as
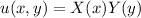
Replace
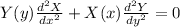
Divide
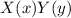
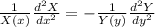
The only way that this can be true, is that every term is the same constant, so we say that
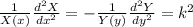
With
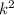 a constant.
a constant.
Now, we solve every part. For
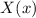
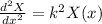
The solution is:
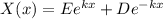
For
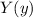
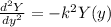
Is the differential equation for a harmonic oscillator, so the solution is
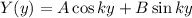
Now, we evaluate the boundary conditions:
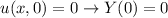
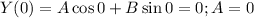
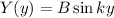
The other
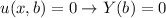
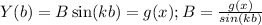
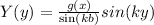
For
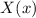 :
:
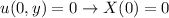
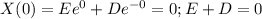
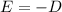
So,
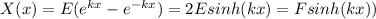
The other condition:
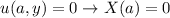
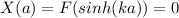
So,