Answer:
v = 7671.57 m/s
T = 1.55 hours
Step-by-step explanation:
mass of Earth, M = 6 x 10^24 kg
Radius of earth, R = 6400 km = 6.4 x 10^6 m
height, h = 400 km
Velocity is given by
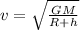
where, G be the universal gravitational constant.
G = 6.657 x 10^-11 Nm^2/kg^2
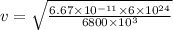
v = 7671.57 m/s
Let T b the period
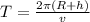
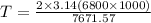
T = 5566.53 second
T = 1.55 hours