Answer:
The appropriate options are:
2. The reaction releases energy.
4.
![[H_(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pbm00a4yz6c0g1jnzxyuesqco11edhipjn.png) and
and
![[I_(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6ujff9tnoxufgogvt6jtuysax8odmm8mf6.png) increase.
increase.
6.
![[HI]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/pq88sisive97yfryuuwflnuopab05pe6a3.png) increases.
increases.
The addition of a non-reacting component C will have no effect on the equilibrium system at constant volume.
Step-by-step explanation:
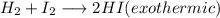
The question can be answered by using Le Chatelier's principle.
According to Le Chatelier's Principle, for a exothermic reaction, decreasing the temperature at equilibrium will cause the forward reaction to occur.
If the forward reaction occurs, subsequently the concentrations of the reactants will decrease and that of the product will increase.
This is the reason for the options 4 and 6 being correct.
Exothermic reactions are the ones that release energy and endothermic reactions are the ones that absorb energy.
Since the forward reaction is exothermic, cooling the reaction mixture at constant volume, will lead to a release of energy.
This is the reason for the option 2 to be correct.
If a component C is added at constant volume, there will be no effect on the equilibrium system, assuming that the component C is non-reacting.
The concentration of that component C will increase, at constant volume.