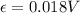Answer:
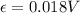
Step-by-step explanation:
given,
Area of rectangular loop = 0.15 m²
Magnetic field = B = 0.20 T
angle between magnetic field and the normal to the plane = π/2
increasing at the rate = 0.60 rad/s
magnitude of emf induced = ?
induce emf through the loop
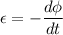
Φ = BA cos θ
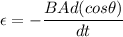
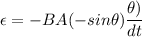
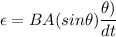
now substituting all the given values
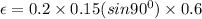
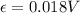
the magnitude of induced emf is equal to