Answer:
The temperature of the nitrogen gas at another section is
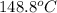
Step-by-step explanation:
Energy balance equation for steady state flow of gas under negiligible potential energy.
The negligible heat transfer and no shaft work is as follows.
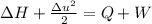
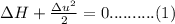
 is enthalphy of gas and it is changes with the temperature.
is enthalphy of gas and it is changes with the temperature.
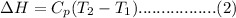
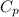 = Molar heat capacity of the gas at constant pressure.
= Molar heat capacity of the gas at constant pressure.
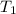 = Initial temperature at section 1
= Initial temperature at section 1
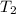 = Final temperature at section 2
= Final temperature at section 2
Substitute the equation (2) in equation (1)
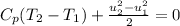
Solve the above equation is as follows.
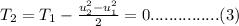
From the given,
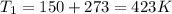
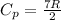
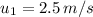
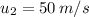
Molar mass of nitrogen gas = 0.02802 kg/mol
Substitute the all values in the equation (3)
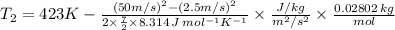
=421.8K=148.8^{o}C
Therefore,The temperature of the nitrogen gas at another section is
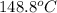 .
.