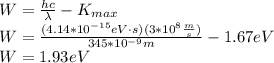Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The maximum kinetic energy of an ejected electron in the photoelectric effect is given by:
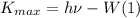
Here h is the Planck's constant,
 the frequency of the light and W the work function of the element.
the frequency of the light and W the work function of the element.
The frequency is equal to the speed of light, divided by the wavelength:
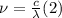
Recall that
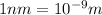 . Replacing (2) in (1) and solving for W:
. Replacing (2) in (1) and solving for W: