Answer:
140.89 L
Step-by-step explanation:
P = Pressure = 44 bar
R = Gas constant = 0.082 L atm/K mol
T = Temperature = 273.15+20 = 293.15 K
W = Volume of water
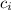 = Initial ion concentration = 1.1 M
= Initial ion concentration = 1.1 M
Final concentration is given by
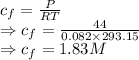
For 1 L of sea water we have
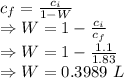
In sea water
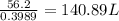
The amount of water needed to produce the freshwater is 140.89 L