Answer:
12.44 mL of 0.1 M acetic acid solution
37.56 mL of 0.1 M sodium acetate solution
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve this problem we can use Henderson-Hasselbach's equation:
- pH = pKa + log [A⁻] / [HA]
Where [A⁻] and [HA] are the molar concentrations of sodium acetate and acetic acid, respectively.
First we use the equation to calculate the molar concentration ratio in the buffer solution:
- 5.2 = 4.72 + log [A⁻] / [HA]
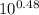 = [A⁻] / [HA]
= [A⁻] / [HA]
We can rewrite the last part, using the definition of molar concentrations (C=n/V):
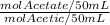 = 3.02
= 3.02
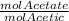 = 3.02
= 3.02
From the problem we also know that:
- Vacetate + Vacetic = 50 mL
We rewirte the equation once again, keeping in mind that the moles of each substance come from the original 0.1 M solutions:
- molAcetate/Macetate + molAcetic/Macetic = 50 mL
- molAcetate/0.1 + molAcetic/0.1 = 0.050 L
So now we have a system of two equations and two unknowns, we use algebra to solve them:
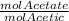 = 3.02
= 3.02
- molAcetate = molAcetic * 3.02
We replace that value in the other equation:
- molAcetate/0.1 + molAcetic/0.1 = 0.050
- molAcetic * 3.02/0.1 + molAcetic/0.1 = 0.050
- 30.2 molAcetic + molAcetic/0.1 = 0.050
- molAcetic = 1.243x10⁻³ mol
We use that value in the first equation:
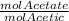 = 3.02
= 3.02
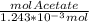 = 3.02
= 3.02
- molAcetate = 3.754x10⁻³ mol
Finally, we use the definition of molarity to calculate the volume of each solution:
- Acetic acid ⇒ 1.243x10⁻³ mol / 0.1 M = 0.0124 L = 12.44 mL
- Acetate ⇒ 3.754x10⁻³ mol / 0.1 M = 0.0375 L = 37.56 mL