Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Velocity of the electron,
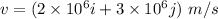
Magnetic field,
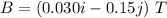
Charge of electron,
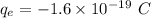
(a) Let
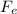 is the force on the electron due to the magnetic field. The magnetic force acting on it is given by :
is the force on the electron due to the magnetic field. The magnetic force acting on it is given by :
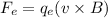
![F_e=1.6* 10^(-19)* [(2* 10^6i+3* 10^6j)* (0.030i-0.15j)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/high-school/t4sjo1700q6dazec8hqf777jy19di19vgx.png)
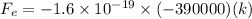
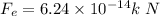
(b) The charge of electron,
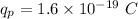
The force acting on the proton is same as force on electron but in opposite direction i.e (-k). Hence, this is the required solution.