Answer:
The temperature of the hot junction is 40.7°C.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Voltage
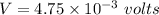
Voltage
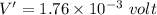
Temperature of hot junction = 110°C
If the voltage is proportional to the difference in temperature between the junctions,
We need to calculate the temperature of the hot junction
Using formula of temperature
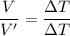
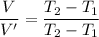
Here,T₁=0°C
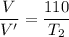
Put the value into the formula
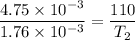
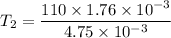
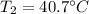
Hence, The temperature of the hot junction is 40.7°C.