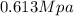To develop this problem it is necessary to apply the concepts related to the calculation of the Force through density and volume as well as the ideal gas law.
By definition, force can be expelled as
F = ma
Where,
m = mass
a = Acceleration
At the same time the mass can be defined as function of density and Volume
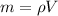
Therefore if we do a sum in the spherical balloon we have,
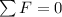
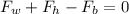
Where,
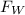 = Force by weight of balloon
= Force by weight of balloon
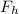 = Force by weight of helium gas
= Force by weight of helium gas
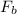 = Buoyant force
= Buoyant force
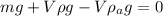
Re-arrange to find
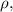
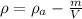
Our values are given as,
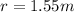
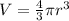
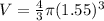
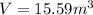
Replacing the values we have,
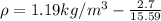
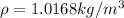
Applying the ideal gas law we have finally that
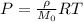
Where,
P = Pressure
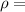 Density
Density
M_0 Molar mass (0.004Kg/mol for helium)
R= Gas constant
T = Temperature
Substituting
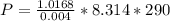
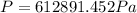
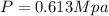
Therefore the absolute pressure of the helium gas is