Answer:
absolute max= (4.243,18)
absolute min =(-1,-5.916)
absolute max=(pi/6, 2.598)
absolute min = (pi/2,0)
Explanation:
a)
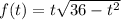
To find max and minima in the given interval let us take log and differentiate
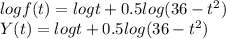
It is sufficient to find max or min of Y
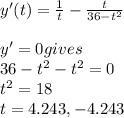
In the given interval only 4.243 lies
And we find this is maximum hence maximum at (4.243,18)
Minimum value is only when x = -1 i.e. -5.916
b)
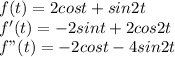
Equate I derivative to 0
-2sint +1-2sin^2 t=0
sint = 1/2 only satisfies I quadrant.
So when t = pi/6 we have maximum
Minimum is absolute mini in the interval i.e. (pi/2,0)