Answer:
25.76 L
Step-by-step explanation:
Given, Volume of Copper = 3.56 cm³
Density = 8.95 g/cm³
Considering the expression for density as:
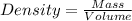
So,
So, Mass= Density * Volume = 8.95 g/cm³ * 3.56 cm³ = 31.862 g
Mass of copper = 31.862 g
Molar mass of copper = 63.546 g/mol
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
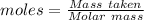
Thus,
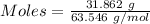
Moles of copper = 0.5014 moles
Given, Volume of nitric acid solution = 200 mL = 200 cm³
Density = 1.42 g/cm³
Considering the expression for density as:
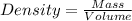
So,
So, Mass= Density * Volume = 1.42 g/cm³ * 200 cm³ = 284 g
Also, Nitric acid is 68.0 % by mass. So,
Mass of nitric acid =
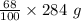 = 193.12 g
= 193.12 g
Molar mass of nitric acid = 63.01 g/mol
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
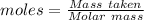
Thus,
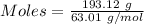
Moles of nitric acid = 3.0649 moles
According to the reaction,
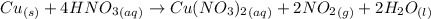
1 mole of copper react with 4 moles of nitric acid
Thus,
0.5014 moles of copper react with 4*0.5014 moles of nitric acid
Moles of nitric acid required = 2.0056 moles
Available moles of nitric acid = 3.0649 moles
Limiting reagent is the one which is present in small amount. Thus, nitric acid is present in large amount, copper is the limiting reagent.
The formation of the product is governed by the limiting reagent. So,
1 mole of copper on reaction forms 2 moles of nitrogen dioxide
So,
0.5014 mole of copper on reaction forms 2*0.5014 moles of nitrogen dioxide
Moles of nitrogen dioxide = 1.0028 moles
Given:
Pressure = 735 torr
The conversion of P(torr) to P(atm) is shown below:
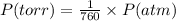
So,
Pressure = 735 / 760 atm = 0.9632 atm
Temperature = 28.2 °C
The conversion of T( °C) to T(K) is shown below:
T(K) = T( °C) + 273.15
So,
T₁ = (28.2 + 273.15) K = 301.35 K
Using ideal gas equation as:
PV=nRT
where,
P is the pressure
V is the volume
n is the number of moles
T is the temperature
R is Gas constant having value = 0.0821 L.atm/K.mol
Applying the equation as:
0.9632 atm × V = 1.0028 mol × 0.0821 L.atm/K.mol × 301.35 K
⇒V = 25.76 L