Answer:
Desision is to not reject the null hypothesis, this means that the variance of the second population is equal or greater than the variance of the first population.
Explanation:
Hello!
You have the hypothesis set:
H₀: δ₁² ≤ δ₂²
H₁: δ₁² > δ₂²
α: 0.01
To study the population variance of two populations you have to work with the F-distribution. The statistic is:
F= (S₁²/S₂²)*(σ₁²/σ₂²) ~ F
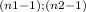
This is a one tailed test, the critical value is
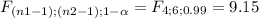
If the statistic value F
 ≥ 9.15, the decision is to reject the null hypothesis.
≥ 9.15, the decision is to reject the null hypothesis.
If the value F
 < 9.15, the decision is to not reject the null hypothesis.
< 9.15, the decision is to not reject the null hypothesis.
F
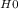 = (S₁²/S₂²)*(σ₁²/σ₂²) = (12/7) * 1
= (S₁²/S₂²)*(σ₁²/σ₂²) = (12/7) * 1
F
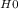 = 1.714
= 1.714
Desision is to not reject the null hypothesis, this means that the variance of the second population is equal or greater than the variance of the first population.
I hope you have a SUPER day!