To develop this problem it is necessary to apply the equations concerning the conservation of the moment.
By definition the moment can be expressed in two ways,
The first as a function of force and because of time, that is
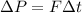
And also based on mass and speed
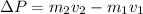
Speed 1 is moving in the opposite direction to our reference system and it remains constant, as is the mass therefore
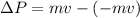
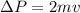
Equation both expression we have that,
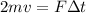
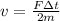
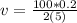
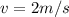
Therefore the speed of the glider is 2m/s