Answer: The vapor pressure of the water when it boils at 50°C is 99.91 mmHg
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the final pressure, we use the Clausius-Clayperon equation, which is:
![\ln((P_2)/(P_1))=(\Delta H_(vap))/(R)[(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4vtbgz8qequ3vvsclhkmmvxlsikmj2gcnu.png)
where,
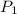 = initial pressure which is the pressure at normal boiling point = 760 mmHg
= initial pressure which is the pressure at normal boiling point = 760 mmHg
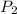 = final pressure = ?
= final pressure = ?
 = Enthalpy of vaporization = 40.65 kJ/mol = 40650 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
= Enthalpy of vaporization = 40.65 kJ/mol = 40650 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
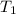 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
![100^oC=[100+273]K=373K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/g6f4bprcfj64kzukkks561wut6ty1cqap8.png)
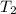 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
![50^oC=[50+273]K=323K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/xw5wlh9dnn1qcql85749mnn9nagg8we7mx.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\ln((P_2)/(760))=(40650J/mol)/(8.314J/mol.K)[(1)/(373)-(1)/(323)]\\\\\ln (P_2)/(760)=-2.029mmHg\\\\(P_2)/(760)=e^(-2.029)=0.1315mmHg\\\\P_2=0.1315* 760=99.91mmHg](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/h5kdnd6avf43g5exlbsmc74h3tlznp4cas.png)
Hence, the vapor pressure of the water when it boils at 50°C is 99.91 mmHg