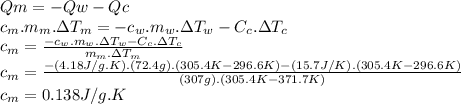Answer:
0.138 J/g.K
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the law of conservation of energy, the sum of the heat released bt he mineral and the heats absorbed by the water and the calorimeter is equal to zero.
Qm + Qw + Qc = 0
Qm = - Qw - Qc [1]
The heat absorbed by the calorimeter can be calculated using the following expression.
Q = C . ΔT
where,
C is the heat capacity
ΔT is the change in temperature
The heat released by the mineral and the one absorbed by the water can be calculated using the following expression.
Q = c . m . ΔT
where,
c is the specific heat capacity
m is the mass
ΔT is the change in temperature
Replacing in [1],