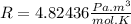Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The Ideal Gas equation is:
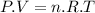 (1)
(1)
Where:
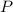 is the pressure of the gas
is the pressure of the gas
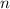 the number of moles of gas
the number of moles of gas
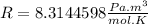 is the gas constant
is the gas constant
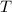 is the absolute temperature of the gas in Kelvin.
is the absolute temperature of the gas in Kelvin.
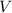 is the volume
is the volume
It is important to note that the behavior of a real gas is far from that of an ideal gas, taking into account that an ideal gas is a single hypothetical gas. However, under specific conditions of standard temperature and pressure (T=0\°C=273.15 K and P=1 atm=101,3 kPa) one mole of real gas (especially in noble gases such as Argon) will behave like an ideal gas and the constant R will be
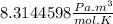 .
.
However, in this case we are not working with standard temperature and pressure, therefore, even if we are working with Argon, the value of R will be far from the constant of the ideal gases.
Having this clarified, let's isolate
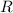 from (1):
from (1):
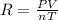 (2)
(2)
Where:
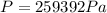
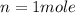
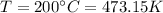 is the absolute temperature of the gas in Kelvin.
is the absolute temperature of the gas in Kelvin.
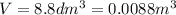
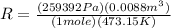 (3)
(3)
Finally: