Answer:
The correct option is: (D) -2.4 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Chemical reaction involved: 2PG ↔ PEP
Given: The standard Gibb's free energy change: ΔG° = +1.7 kJ/mol
Temperature: T = 37° C = 37 + 273.15 = 310.15 K (∵ 0°C = 273.15K)
Gas constant: R = 8.314 J/(K·mol) = 8.314 × 10⁻³ kJ/(K·mol) (∵ 1 kJ = 1000 J)
Reactant concentration: 2PG = 0.5 mM
Product concentration: PEP = 0.1 mM
Reaction quotient:
![Q_(r) =(\left [ PEP \right ])/(\left [ 2PG \right ]) = (0.1 mM)/(0.5 mM) = 0.2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qqwa4tmkmgs6sdfwaqofh7afawfuukmwsx.png)
To find out the Gibb's free energy change at 37° C (310.15 K), we use the equation:
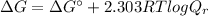
![\Delta G = 1.7 kJ/mol + [2.303 * (8.314 * 10^(-3) kJ/(K.mol))* (310.15 K)] log (0.2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/z98j5pp3bhd2z7u7h3txb9zg4j0xs7aojv.png)
![\Delta G = 1.7 + [5.938] * (-0.699) = 1.7 - 4.15 = (-2.45 kJ/mol)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/i37c1cz2vlpg6ji3b6lqwsnmnx4kq50793.png)
Therefore, the Gibb's free energy change at 37° C (310.15 K): ΔG = (-2.45 kJ/mol)