Answer:
infinity
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that
Resistance = R
Resistivity = ρ
Length = L
Diameter = d
The resistance of wire R given as
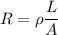
A=Area
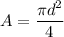
Now by putting the value of A
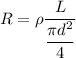
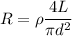
When d tends to infinity then d² will also tends to infinity.
So when d tends to zero then the resistance tends to infinity.
Therefore answer is ---
infinity