Answer:
The heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter is 7.58 J/°C.
Step-by-step explanation:
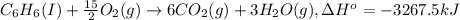
First, we will calculate energy released on combustion:
 = enthalpy change = -3267.5 kJ/mol
= enthalpy change = -3267.5 kJ/mol
q = heat energy released
n = number of moles benzene=
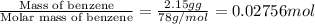
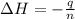
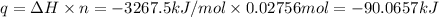
q = -90.0657 kJ = -90,065.7 J
Now we calculate the heat gained by the calorimeter let it be Q.
Q = -q= -(-90,065.7 J) = 90,065.7 J (conservation of energy)
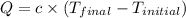
where,
Q = heat gained by calorimeter
c = specific heat capacity of calorimeter =?
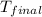 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
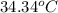
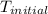 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
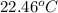
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
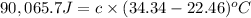
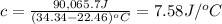
The heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter is 7.58 J/°C.